As our globe grapples with the escalating crisis of plastic pollution, an innovative solution has emerged, captivating audiences worldwide. Climate-positive content creator Sam Bentley recently shed light on the groundbreaking technology of the Manta, a plastic-eating boat developed by the ocean depollution organization, The Sea Cleaners.
In his viral video, Bentley reveals the mechanics of the Manta, revealing its ability to operate for up to 20 hours a day through a combination of solar and wind power. Notably, the boat incorporates a waste-to-energy conversion unit, turning collected plastic into fuel, providing a sustainable source of power. The Manta can extract an impressive three tons of plastic waste from the ocean every hour, subsequently sorting it into various material categories like plastics, glass, and aluminum for recycling on land.
Highlighting additional features, Bentley emphasizes the installation of a crane on the Manta to lift larger polluting items from the water, and smaller boats designed for skimming plastic waste in shallow waters. This multifaceted approach underscores the boat’s efficiency and adaptability in addressing the pervasive issue of plastic Pollution.
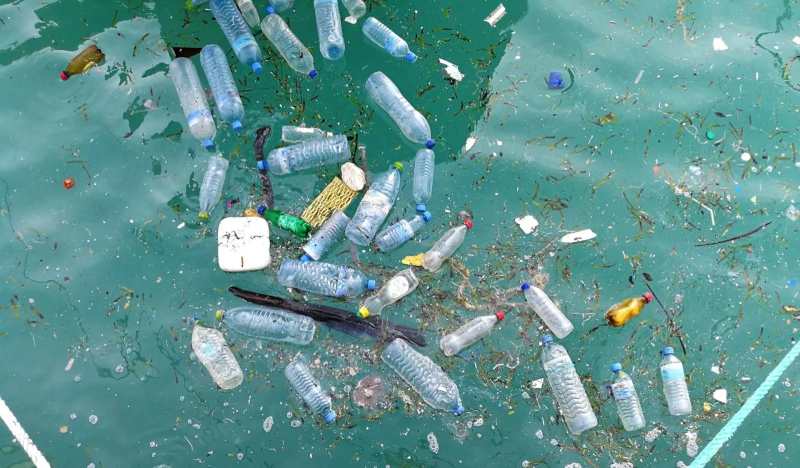
The Sea Cleaners reports a staggering statistic: 1.5 million marine animals succumb to plastic Pollution each year. Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the Manta stands out as a powerful tool in the fight against the toxic chemicals leaching into water supplies and the accumulation of harmful microplastics affecting marine habitats.
According to The Sea Cleaners, a staggering 380 million tons of plastic are produced globally each year, with half of this amount comprising single-use products. Shockingly, up to 32% of plastic waste finds its way into nature, posing a severe threat to the oceans, which witness an annual influx of nine to 14 tons of plastic.
While the Manta offers a promising solution to the existing plastic Pollution crisis, the imperative to reduce plastic production and consumption remains paramount. Most plastics derive from environmentally harmful sources like oil, contributing significantly to planet-warming gases. Moreover, the production process involves toxic substances, posing health risks to humans in regular contact with the material.
Source: onegreenplanet.org